Food packaging is a ubiquitous part of our daily lives, shaping our choices and perceptions about the products we consume. While labels may seem straightforward at first glance, delving deeper reveals a complex world of ingredients, nutritional information, and marketing strategies. Understanding the intricacies behind food packaging is crucial for making informed decisions about what we eat. In this article, we will explore the various elements of food labels and ingredients, shedding light on their significance and impact on our health and well-being.
Deciphering Food Labels
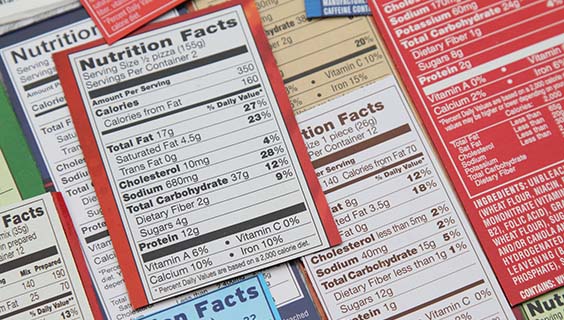
Food labels serve as the primary means of communication between manufacturers and consumers. They provide essential information about the product’s contents, nutritional value, and serving sizes. However, navigating through these labels can be challenging, as they often contain a plethora of terms and numbers. To decipher food labels effectively, it’s essential to understand the key components.
At the forefront of any food label is the list of ingredients. This section outlines the components used in the product’s formulation, listed in descending order of predominance by weight. Ingredients are typically accompanied by their scientific names, which may be unfamiliar to the average consumer. For example, sodium chloride is commonly known as table salt. Understanding these terms can help consumers identify potential allergens or additives they wish to avoid.
In addition to ingredients, food labels also provide nutritional information per serving. This includes details such as calories, fat content, carbohydrates, protein, and micronutrients like vitamins and minerals. These values offer valuable insights into the nutritional profile of the product and can assist consumers in making healthier choices. However, it’s essential to pay attention to serving sizes, as they can vary significantly and affect the accuracy of nutritional calculations. It’s like how a test prep program in Bettendorf helps students navigate through their academic challenges with tailored strategies and support.
The Role of Packaging
Beyond its functional purpose of containing and protecting food products, packaging plays a significant role in marketing and branding. The design, color scheme, and imagery used on packaging can influence consumer perceptions and purchasing decisions. From vibrant graphics to eco-friendly materials, packaging serves as a visual cue that communicates the product’s identity and values.
Packaging also serves as a platform for conveying additional information about the product, beyond what is stated on the label. This may include promotional messages, health claims, or certifications such as organic or non-GMO. While these elements can enhance the appeal of a product, consumers should approach them with a critical eye and seek out substantiated information to verify their validity.
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on sustainable packaging solutions that minimize environmental impact. From recyclable materials to biodegradable packaging, manufacturers are exploring innovative ways to reduce waste and carbon footprint. By supporting brands that prioritize sustainability, consumers can contribute to positive change and encourage industry-wide adoption of eco-conscious practices, including the production of window blinds in Colorado Springs.
Navigating Ingredient Lists
Understanding the ingredients listed on food labels is essential for making informed choices about the products we consume. However, deciphering these lists can be daunting, especially when faced with unfamiliar terms and additives. To navigate ingredient lists effectively, it’s helpful to familiarize oneself with common additives and their potential implications for health.
One category of ingredients that often raises concerns among consumers is additives. These substances are added to food products to enhance flavor, texture, appearance, or shelf life. While many additives are deemed safe for consumption by regulatory agencies, some may have adverse effects on health, particularly in high quantities. Examples include artificial colors, preservatives, and flavor enhancers, which have been linked to various health issues in studies.
In addition to additives, ingredient lists may also contain terms that denote allergens or dietary restrictions. For individuals with food sensitivities or allergies, carefully reviewing ingredient lists is crucial to avoid potential adverse reactions. Common allergens such as peanuts, gluten, and dairy are often highlighted in bold or specified separately to alert consumers to their presence in the product. Effective visual communications can play a significant role in ensuring consumers quickly identify and understand these crucial details.
Interpreting Nutrition Labels

Nutrition labels provide vital information about the nutritional content of food products, helping consumers make informed choices to support their health and well-being. Understanding how to interpret these labels is key to unlocking their full potential in guiding dietary decisions. One aspect to consider is the serving size, which determines the quantity of nutrients listed on the label. It’s important to note that serving sizes may not always align with typical consumption patterns, so adjusting portions accordingly is essential for accurate nutritional assessment. Additionally, pay attention to the percent daily values (%DV) provided on the label, which indicate how much a nutrient contributes to a daily diet based on a 2,000-calorie-per-day reference diet. This can help individuals gauge the relative importance of each nutrient in the context of their overall diet.
Beyond serving sizes and %DV, consumers should also examine the specific nutrients listed on the label. While some nutrients, such as fiber and certain vitamins, are beneficial for health, others, like saturated fat and added sugars, should be consumed in moderation. By comparing the nutritional profiles of different products, consumers can make choices that align with their dietary goals and preferences. Additionally, consider the ingredient list to identify any potential allergens or undesirable additives. Armed with this knowledge, consumers can confidently navigate the grocery aisle and select products that support their health and well-being, while keeping in mind the importance of flood emergency restoration in Charlotte.
Unveiling Marketing Tactics
Food packaging is not only a container for products but also a powerful tool for marketing and promotion. Manufacturers employ various tactics to attract consumers’ attention and influence their purchasing decisions. One common strategy is the use of buzzwords like “natural,” “organic,” or “gluten-free” to appeal to health-conscious consumers. While these terms may imply certain qualities about the product, it’s essential to scrutinize the label and verify the legitimacy of such claims. Additionally, packaging design plays a significant role in shaping consumer perception. Bright colors, sleek fonts, and appealing imagery can create an emotional connection with the product, prompting impulse purchases. By understanding the marketing tactics employed on food packaging, consumers can approach product selection with a critical eye and make choices that align with their preferences and values.
Moreover, consumers should be aware of deceptive marketing practices that may mislead them into believing a product is healthier or more environmentally friendly than it actually is. For example, terms like “low-fat” or “all-natural” may create a perception of healthfulness, even if the product is high in sugar or contains artificial ingredients. Similarly, images of lush farms or picturesque landscapes on packaging may evoke a sense of sustainability, despite the product’s actual environmental impact. By educating themselves about common marketing tactics and reading labels with a discerning eye, consumers can make more informed choices and avoid falling prey to misleading advertising. This applies to various consumer goods, including vacation home rentals, where enticing descriptions and attractive imagery may not always reflect the true quality or sustainability of the accommodation.
Exploring Ingredient Transparency
In recent years, there has been a growing demand for transparency in food production and labeling. Consumers are increasingly interested in knowing where their food comes from and how it’s made. Ingredient transparency refers to the practice of disclosing detailed information about the sourcing and processing of ingredients used in food products. This includes providing information about farming practices, production methods, and supply chain traceability. By prioritizing ingredient transparency, brands can build trust and credibility with consumers who value authenticity and accountability in food production. Additionally, ingredient transparency promotes greater awareness of food quality and safety, empowering consumers to make choices that support their health and ethical values. Embracing ingredient transparency is as essential as the precision required in paver sealing in St. Augustine, FL.
Furthermore, ingredient transparency extends beyond the list of ingredients to encompass broader issues such as fair labor practices, animal welfare, and environmental sustainability. Consumers are increasingly seeking products that align with their values and beliefs, driving demand for ethically sourced and responsibly produced goods. By providing transparent information about ingredient sourcing and production practices, brands can demonstrate their commitment to social and environmental responsibility, fostering trust and loyalty among consumers. Ultimately, ingredient transparency benefits not only consumers but also the food industry as a whole, encouraging greater accountability and sustainability throughout the supply chain.
Ensuring the best Japanese scissors are used in packaging can reflect a commitment to quality craftsmanship and support for traditional artisans, aligning with consumer preferences for high-quality, culturally significant products.
Navigating Dietary Restrictions
For individuals with dietary restrictions or special dietary needs, navigating food labels can be particularly challenging. Whether due to allergies, intolerances, or lifestyle choices, understanding ingredient lists is crucial for avoiding potential allergens or undesired ingredients. Some common dietary restrictions include gluten-free, dairy-free, vegan, and kosher. Fortunately, many food manufacturers now offer products specifically formulated to meet these dietary needs, with clear labeling to indicate their suitability. Additionally, online resources and smartphone apps can be valuable tools for quickly identifying safe products while shopping. By staying informed and vigilant, individuals with dietary restrictions can confidently navigate the grocery aisle and enjoy a diverse range of food options that align with their dietary preferences and requirements. When it comes to choosing attire, individuals may also seek specific options, such as womens waffle robes, ensuring both comfort and style in their wardrobe selections.
Moreover, individuals with dietary restrictions should be proactive in advocating for their needs and communicating with food manufacturers and retailers. By providing feedback and requesting more options that cater to their dietary requirements, consumers can drive positive change within the industry and ensure greater accessibility to safe and suitable food products. Additionally, community support groups and online forums can be valuable sources of information and encouragement for individuals navigating dietary restrictions. By sharing experiences and resources, individuals can learn from each other and discover new strategies for managing their dietary needs effectively. Ultimately, by fostering a supportive and inclusive environment, we can empower individuals with dietary restrictions to lead healthy and fulfilling lives.
Staying connected with online communities that share updates on various interests, such as bass fishing forecast, can provide individuals with a sense of belonging and access to diverse resources to enhance their overall well-being.
Embracing Sustainable Packaging

In response to growing environmental concerns, there has been a notable shift towards sustainable packaging solutions in the food industry. Sustainable packaging aims to minimize waste, reduce carbon footprint, and promote environmental stewardship throughout the product lifecycle. This includes using recyclable, compostable, or biodegradable materials, as well as optimizing packaging design to minimize excess packaging and maximize resource efficiency. By embracing sustainable packaging practices, food manufacturers can demonstrate their commitment to environmental responsibility and meet the evolving expectations of consumers who prioritize sustainability. Additionally, consumers can support these efforts by choosing products packaged in eco-friendly materials and advocating for sustainability initiatives within the food industry.
Furthermore, sustainable packaging extends beyond material choices to encompass broader issues such as packaging waste management and circular economy principles. Recycling and composting programs can help divert packaging materials from landfills and reduce environmental pollution. Additionally, innovative approaches such as reusable packaging and package-free shopping are gaining traction as alternatives to traditional single-use packaging. By embracing these solutions, food manufacturers and retailers can minimize their environmental impact and contribute to a more sustainable future. Moreover, collaboration across the supply chain is essential for driving systemic change and implementing scalable solutions that address the root causes of packaging waste. By working together towards common goals, we can create a more resilient and sustainable food system for future generations.
Incorporating eco-friendly transportation options, such as electric delivery vans, and partnering with companies that offer sustainable logistics solutions like rent a car Sarajevo, can further reduce the carbon footprint associated with food packaging distribution.
Conclusion
Understanding food packaging and ingredient labels is essential for making informed choices about the products we consume. From deciphering nutrition labels to scrutinizing marketing tactics and embracing sustainable packaging, each aspect plays a crucial role in shaping consumer perceptions and behaviors. By equipping ourselves with knowledge and awareness, we can navigate the grocery aisle with confidence, selecting products that support our health, values, and sustainability goals. Ultimately, by fostering transparency, accountability, and sustainability within the food industry, we can collectively contribute to a healthier, more equitable, and more sustainable future for all.
